# 基础
# HTML
# 如何理解 HTML 语义化
- 让人更容易读懂(增加代码可读性)
- 让搜索引擎更容易读懂 ( SEO)
# 块状元素 &内联元素
- display: block/table; 有 div h1 h2 table ul ol p 等
- display: inline/inline-block;有 span img input button 等
# CSS
# 盒模型宽度计算
offsetWidth = (内容宽度 + 内边距 + 边框),无外边距
offsetHeight = (内容高度 + 内边距 + 边框),无外边距
# margin 纵向重叠问题
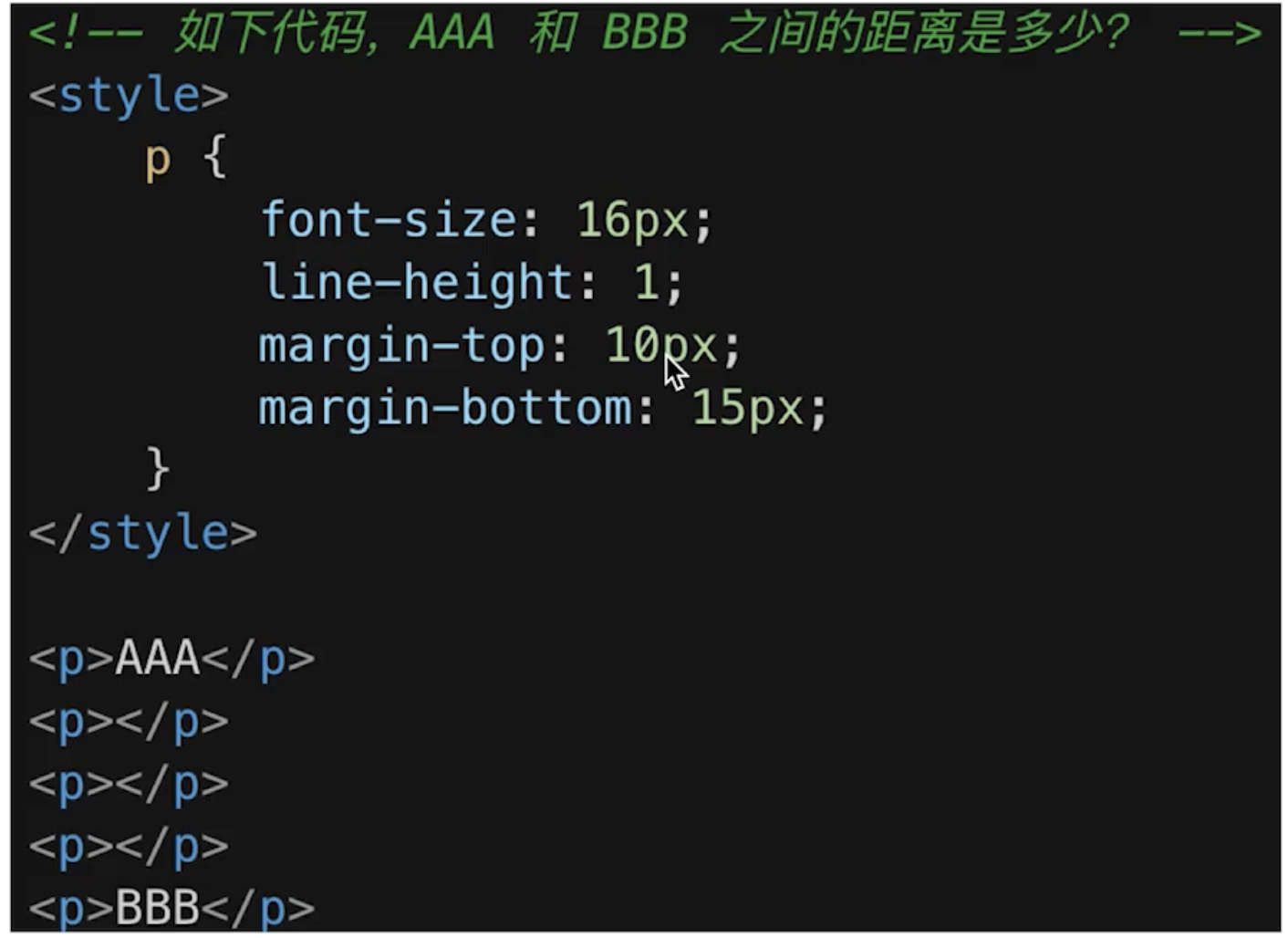
- 相邻元素的 margin-top 和 margin-bottom 会发生重叠
- 空白内容的
<p></p>也会重叠 - 答案:15px
# margin 负值问题
- margin-top 和 margin-left 负值,元素向上、向左移动
- margin-right 负值,右侧元素左移,自身不受影响
- margin-bottom 负值,下方元素上移,自身不受影响
# BFC 理解与应用
# 概念
- Block format context,块级格式化上下文
- 一块独立渲染区域,内部元素的渲染不会影响边界以外的元素
# BFC 常见形成条件
- float 不是 none
- position 是 absolute 或 fixed
- overflow 不是 visible
- display 是 flex inline-block 等
# BFC 常见应用
清除浮动
# float 布局
# 如何实现圣杯布局和双飞翼布局
圣杯布局和双飞翼布局的目的
- 三栏布局,中间一栏最先加载和渲染(内容最重要)
- 两侧内容固定,中间内容随着宽度自适应
- 一般用于 PC 网页
圣杯布局和双飞翼布局的技术总结
- 使用 float 布局
- 两侧使用 margin 负值,以便和中间内容横向重叠
- 防止中间内容被两侧覆盖,一个用 padding 一个用 margin
<!-- 圣杯布局 -->
<!-- 利用padding完成 -->
<style>
.container {
padding-left: 200px;
padding-right: 150px;
}
.main {
background-color: yellow;
float: left;
width: 100%;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
float: left;
margin-left: -100%;
position: relative;
left: -200px;
}
.right {
width: 150px;
background-color: blue;
float: left;
margin-right: -150px;
}
</style>
<div class="container">
<div class="main">中间内容</div>
<div class="left">左边</div>
<div class="right">右边</div>
</div>
<!-- 双飞翼布局 -->
<!-- 利用marin完成 -->
<style>
.container {
background-color: yellow;
width: 100%;
float: left;
}
.main {
margin-left: 200px;
margin-right: 150px;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
background-color: red;
float: left;
margin-left: -100%;
}
.right {
width: 150px;
background-color: blue;
float: left;
margin-left: -150px;
}
</style>
<div class="container">
<div class="main">中间内容</div>
</div>
<div class="left">左边</div>
<div class="right">右边</div>
# 手写 clearfix
footer 为需要清除浮动的元素
<div class="container clearfix">
<div class="main">中间内容</div>
<div class="left">左边</div>
<div class="right">右边</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
.clearfix:after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
# flex 画骰子
主要利用align-self属性,允许单个项目有与其他项目不一样的对齐方式,可覆盖align-items属性。默认值为auto,表示继承父元素的align-items属性,如果没有父元素,则等同于stretch
<style>
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
width: 120px;
height: 120px;
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 10px;
}
.item {
background-color: #666;
border-radius: 50%;
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
}
.second {
align-self: center;
}
.last {
align-self: flex-end;
}
</style>
<div class="container">
<div class="item"></div>
<div class="item second"></div>
<div class="item last"></div>
</div>
# css 定位
# absolute 和 relative 定位
- relative 依据自身定位
- absolute 依据最近一层的定位元素定位(absolute relative fixed body)
# 居中对齐的实现方式
# 水平居中
- inline 元素:text-align:center
- block 元素:margin:auto
- absolute 元素:left: 50% + margin-left 负值
# 垂直居中
- inline 元素:line-height 的值等于 height 值
- absolute 元素:top:50% + margin-top 负值
- absolute 元素:transform(-50%,-50%)
- absolute 元素:top, left, bottom, right = 0 + margin:auto
# line-height 如何继承
- 写具体数值,如 30px,则继承该值
- 写比例,如 2/1.5,则继承该比例
- 写百分比,如 200%,则继承计算出来的值
line-height 继承父元素百分比行高时,先进行计算再继承给子元素
.father {
font-size: 20px;
line-height: 200%;
}
.son {
font-size: 16px;
/* 子元素继承来的行高为20*200%=40 */
}
# JS
# 数据类型
# 实现深拷贝
function deepClone(obj) {
if (typeof obj !== "object" || obj === null) {
return obj;
}
let result;
if (obj instanceof Array) {
result = [];
} else {
result = {};
}
for (const key in obj) {
// 保证key不是原型的属性
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
// 递归调用
result[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
return result;
}
# 原型和原型链
# 类型判断 instanceof
[] instanceof Array; // true
[] instanceof Object; // true
{} instanceof Object // true
# 原型
// class 实际上是函数,可见是语法糖
typeof People; // 'function'
typeof Student; // 'function'
// 隐式原型和显式原型
console.log(xialuo.__proto__);
console.log(Student.prototype);
console.log(xialuo.__proto__ === Student.prototype); // true
- 每个 class 都有显式原型 prototype
- 每个实例都有隐式原型
__proto__ - 实例的
__proto__指向对应 class 的 prototype
# 作用域和闭包
# 自由变量
- 一个变量在当前作用域没有定义,但被使用了
- 向上级作用域,一层一层依次寻找,直至找到为止
- 如果到全局作用域都没找到,则报错 xxx is not defined
# 闭包
作用域应用的特殊情况,有两种表现:
- 函数作为参数被传递
- 函数作为返回值被返回
所有自由变量的查找,是在函数定义的地方向上级作用域查找,不是在执行的地方
# this
this 取值为执行的地方决定

# 手写 bind 函数
// 模拟bind
Function.prototype.bind1 = function() {
// 将参数拆解为数组
const args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments);
// 或者用...运算符
// const args = [...arguments].slice(1);
// 获取this(即数组第一项)
const t = args.shift();
// fn.bind(...)中的fn
const self = this;
// 返回一个函数
return function() {
return self.apply(t, args);
};
};
# 异步和单线程
# 异步和同步
- 基于 JS 是单线程语言
- 异步不会阻塞代码执行
- 同步会阻塞代码执行
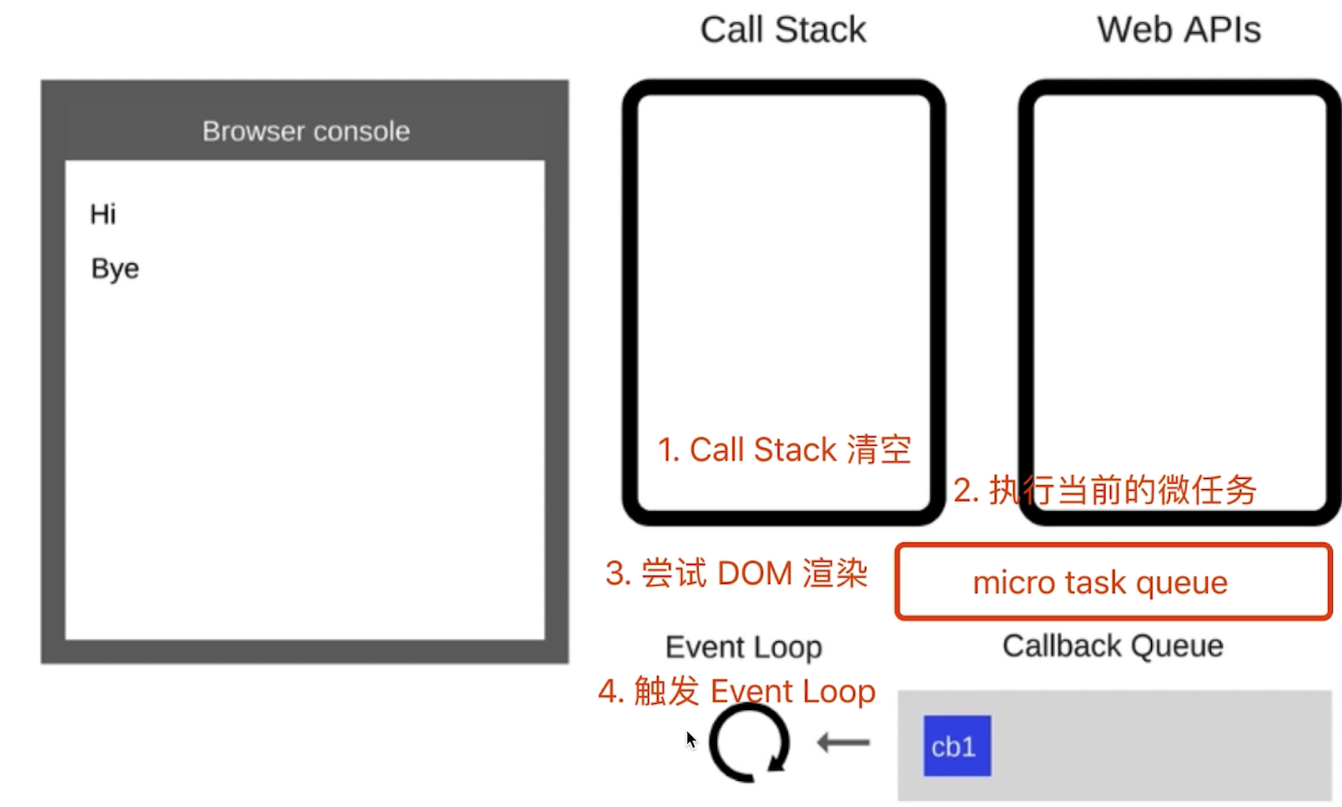
# event loop( 事件循环/事件轮询)
- 同步代码,一行一行放在 Call Stack 执行
- 遇到异步,会先“记录”下,等待时机(定时、网络请求等)
- 时机到了,就移动到 Callback Queue
- 如 Call Stack 为空(即同步代码执行完)Event Loop 开始工作
- 轮询查找 Callback Queue,如有则移动到 Call Stack 执行
- 然后继续轮询查找(永动机一样)
# promise then 和 catch 的连接
- promise 三种状态(pending、fulfilled、rejected)
- pending 状态,不会触发 then 和 catch
- fulfilled 状态,会触发后续的 then 回调函数
- rejected 状态,会触发后续的 catch 回调函数
# then 和 catch 改变状态
- then 正常返回 fulfilled,里面有报错则返回 rejected
const p1 = Promise.resolve().then(() => {
return 100;
});
// p1执行后为fulfilled
const p2 = Promise.resolve().then(() => {
throw new Error("抛出错误");
});
// p2执行后为rejected
- catch 正常返回 fulfilled, 里面有报错则返回 rejected
const p3 = Promise.reject("错误").catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
});
// p3执行后为fulfilled
const p4 = Promise.reject("错误").catch((err) => {
throw new Error(111);
});
// p4执行后为rejected
# 面试题
// 第一題
Promise.resolve()
.then(() => {
console.log(1);
// 返回 fulfilled 不进入 catch
})
.catch(() => {
console.log(2);
})
.then(() => {
console.log(3);
});
// 1 3
// 第二題
Promise.resolve()
.then(() => {
console.log(1);
throw new Error("error1");
// 返回 rejected 进入 catch
})
.catch(() => {
console.log(2);
// 返回 fulfilled 进入 then
})
.then(() => {
console.log(3);
});
// 1 2 3
// 第三題
Promise.resolve()
.then(() => {
console.log(1);
throw new Error("error1");
// 返回 rejected 进入 catch
})
.catch(() => {
console.log(2);
// 返回 fulfilled 不进入 catch
})
.catch(() => {
console.log(3);
});
// 1 2
# async/await 和 Promise 的关系
- 执行 async 函数,返回的是 Promise 对象
- await 相当于 Promise 的 then
- try...catch 可捕获异常,代替了 Promise 的 catch
(async function() {
const p = Promise.reject("错误");
const result = await p; // await相当于then,不会打印console
console.log("result", result);
});
# for...of
function muti(num) {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * num);
}, 1000);
});
}
const nums = [1, 2, 3];
// 一秒钟打印 1 4 9,因为forEach是同步的
// nums.forEach(async (i) => {
// const res = await muti(i);
// console.log(res);
// });
// 每隔一秒钟打印 1 4 9
(async function() {
for (const i of nums) {
const res = await muti(i);
console.log(res);
}
})();
# 宏任务和微任务
- 宏任务:setTimeout、setInterval、Ajax、DOM 事件,在 DOM 渲染后触发
- 微任务:Promise、async/await,在 DOM 渲染前触发
- 微任务执行时机比宏任务要早
# DOM 相关
# DOM 性能
- 对 DOM 查询做缓存
- 将频繁操作改为一次性操作
# BOM 相关
# location 和 history
// location
console.log(location.href);
console.log(location.protocol); // 'http:' 'https:
console.log(location.pathname); // '/learn/199'
console.log(location.search);
console.log(location.hash);
// history
history.back();
history.forward();
# 事件相关
阻止事件冒泡-event.stopPropagation()
阻止事件默认行为-event.preventDefault()
# 事件代理
// 通用事件绑定函数
function bindEvent(elem, type, selector, fn) {
if (fn == null) {
fn = selector;
selector = null;
}
elem.addEventListener(type, (event) => {
const target = event.target;
if (selector) {
// 代理绑定
if (target.matches(selector)) {
fn.call(target, event);
}
} else {
fn.call(target, event);
}
});
}
// 事件代理,监听父元素事件
const div3 = document.getElementById("div3");
bindEvent(div3, "click", "div", function() {
console.log(this.innerHTML);
});
# ajax
# ajax 简单实现
get 请求
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("get", "http://zhangblog.cn:7001/recommend/banner", true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
}
};
xhr.send();
post 请求
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("post", "http://zhangblog.cn:7001/recommend/banner", true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(xhr.responseText);
}
}
};
const postData = {
username: "abc",
};
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(postData));
xhr.readyState
- 0-(未初始化)还没有调用 send() 方法
- 1-(载入)已调用 send() 方法,正在发送请求
- 2-(载入完成)send() 方法执行完成,已经接收到全部响应内容
- 3-(交互)正在解析响应内容
- 4-(完成)响应内容解析完成,可以在客户端调用
xhr.status
- 2xx - 表示成功处理请求,如 200
- 3xx - 需要重定向,浏览器直接跳转,如 301 302 304
- 4xx - 客户端请求错误,如 404 403
- 5xx - 服务器端错误
# 同源策略
- ajax 请求时,浏览器要求当前网页和 server 必须同源(安全)
- 同源:协议、域名、端口,三者必须一致
- 加载图片 css js 可无视同源策略
<img src="跨域的图片地址" />
<link href="跨域的css地址" />
<script src='跨域的js地址'></script>
# 跨域
所有的跨域,都心须经过 server 端允许和配合。未经 server 端允许就实现跨域,说明浏览器有漏洞
- jsonp 实现跨域
// jsonp.js 运行在8080端口
callback({ name: "zhangsan" });
<!-- test.html 运行在5500端口 -->
<script>
window.callback = function(data) {
console.log(data);
};
</script>
<script src="http://localhost:8080/jsonp.js"></script>
<!-- 返回执行callback方法 -->
- CORS 服务器设置 http header
// 第二个参数填写允许跨域的域名称,不建议直接写"*"
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://localhost:8011");
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "X-Requested-With");
response.setHeader(
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods",
"PUT, POST, GET, DELETE, OPTIONS"
);
// 接收跨域的cookie
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");
# 存储
# cookie
- 存储大小,最大 4KB
- http 请求时需要发送到服务端,增加请求数据量
- 只能用
document.cookie='...'来修改,太过简陋
# localStorage 和 sessionStorage
- HTML5 专门为存储而设计,最大可存 5M
- API 简单易用 setItem getItem
- 不会随着 http 请求被发送出去
区别:
- localStorage 数据会永久存储,除非代码或手动删除
- sessionStorage 数据只存在于当前会话,浏览器关闭则清空
- 一般用 localStorage 会更多一些
- sessionStorage 不在不同的浏览器窗口中共享,即使是同一个页面;localStorage 在所有同源窗口中都是共享的;cookie 也是在所有同源窗口中都是共享的
# HTTP
# http 状态码
- 1xx 服务器收到请求
- 2xx 请求成功,如 200
- 3xx 重定向,如 302
- 4xx 客户端错误,如 404
- 5xx 服务端错误,如 500
# 常见状态码
- 200 成功
- 301 永久重定向(配合 location,浏览器自动处理)
- 302 临时重定向(配合 location, 浏览器自动处理)
- 304 资源未被修改
- 403 没有权限
- 404 资源未找到
- 500 服务器错误
- 504 网关超时
# http methods
- get 获取数据
- post 新建数据
- patch/put 更新数据
- delete 删除数据
# Restful API
- 传统 API 设计:把每个 url 当做一个功能
- Restful API 设计: 把每个 url 当做一个唯一的资源
对比
传统 API 设计:/api/list?pageIndex=2
Restful API 设计:/api/list/2
# http headers
# Request Headers
- Accept 浏览器可接收的数据格式
- Accept-Encoding 浏览器可接收的压缩算法,如 gzip
- Accept-Language 浏览器可接收的语言,如 zh-CN
- Connection: keep-alive 一次 TCP 连接重复使用
- cookie
- Host
- User-Agent(简称 UA)浏览器信息
- content-type 发送数据的格式,如 application/json
# Response Headers
- Content-type 返回数据的格式,如 application/json
- Content-length 返回数据的大小,多少字节
- Content-Encoding 返回数据的压缩算法 ,如 gzip
- Set-Cookie
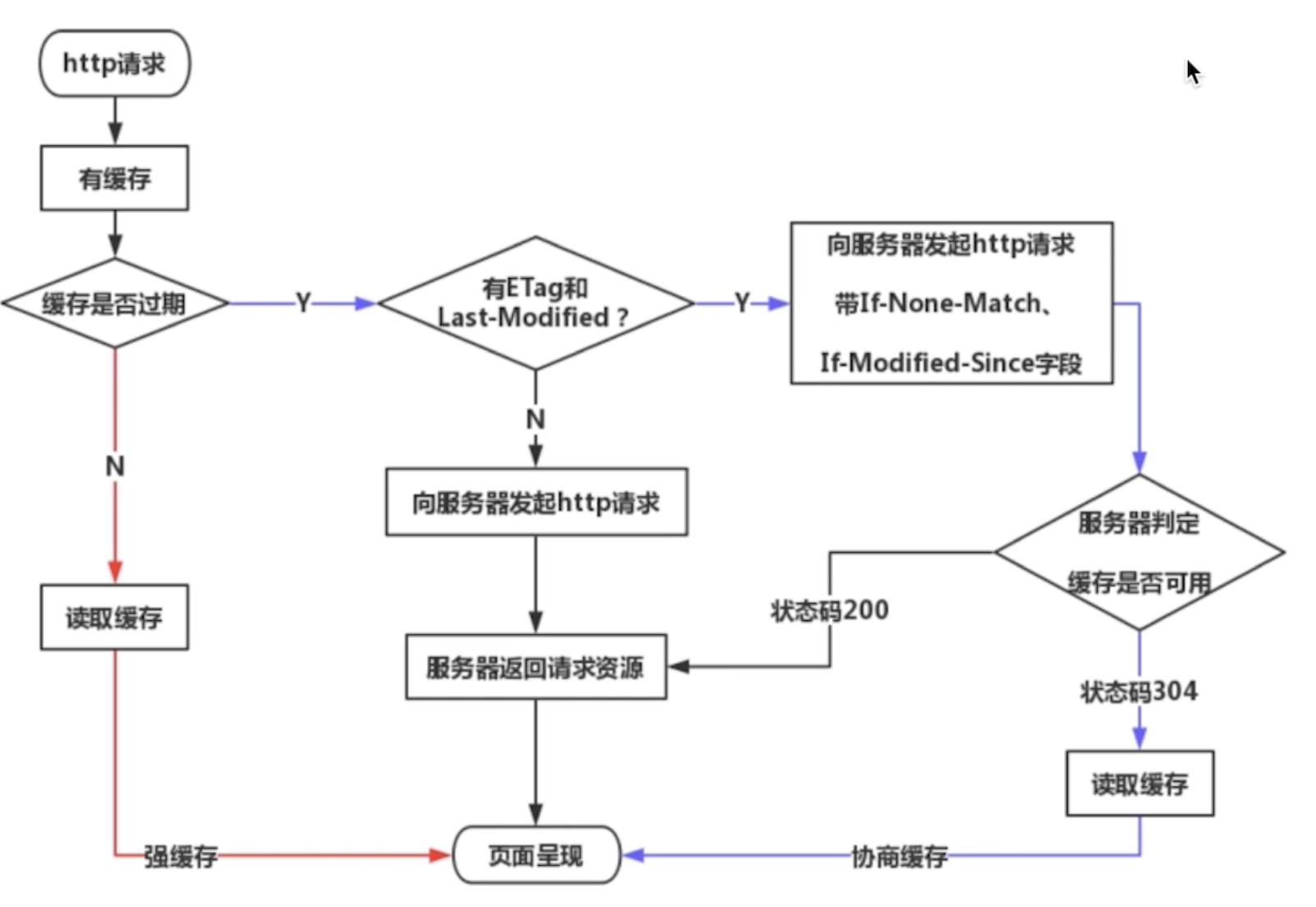
# http 缓存
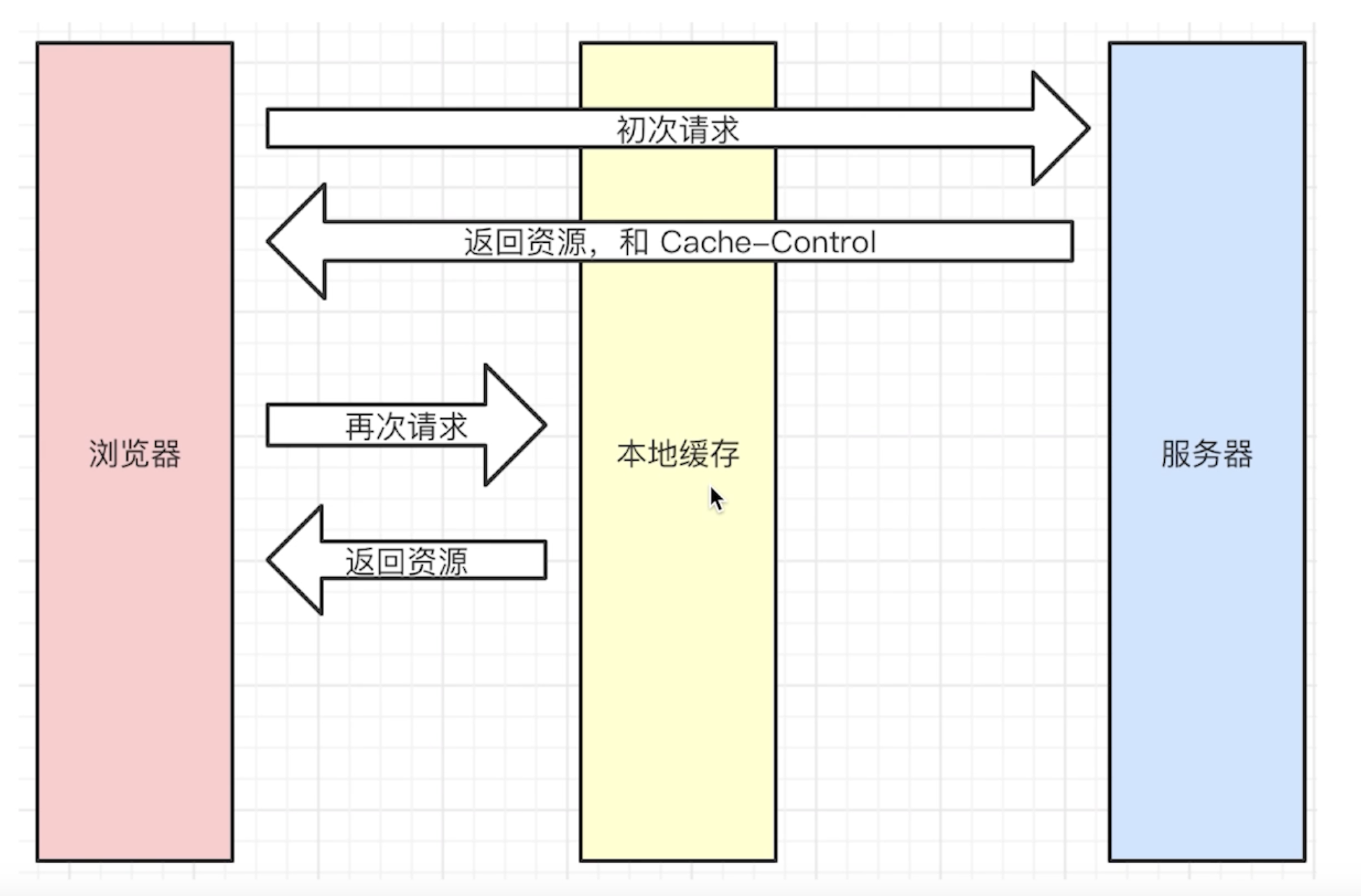
# 强制缓存
存在 Response Headers 中,控制强制缓存的逻辑,例如 Cache-Control: max-age=31536000(单位是秒)
# cache-control 的值
- max-age
- no-cache
- no-store
- private
- public
# 关于 Expires
- 同在 Response Headers 中
- 同为控制缓存过期
- 已被 Cache-Control 代替
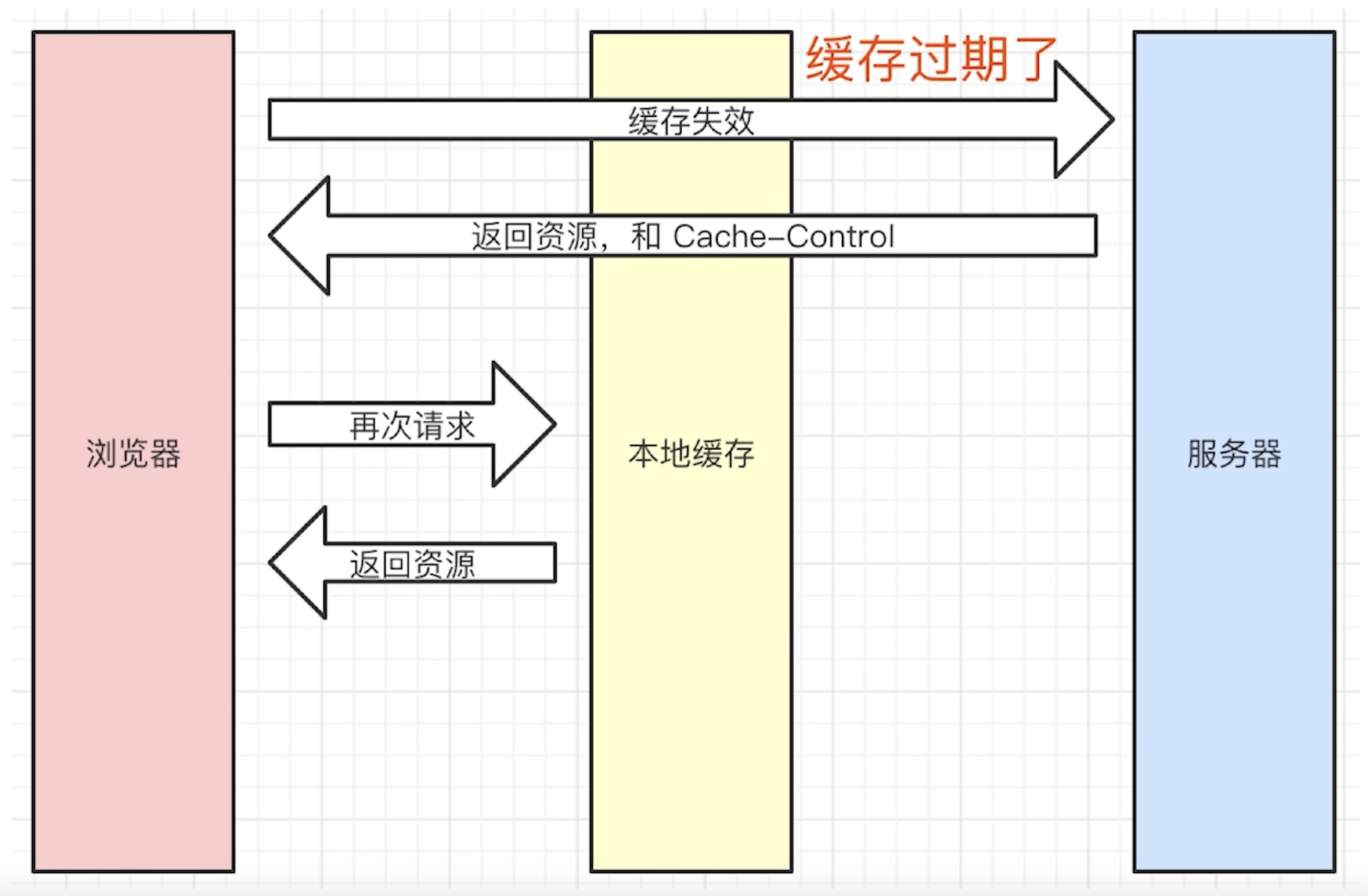
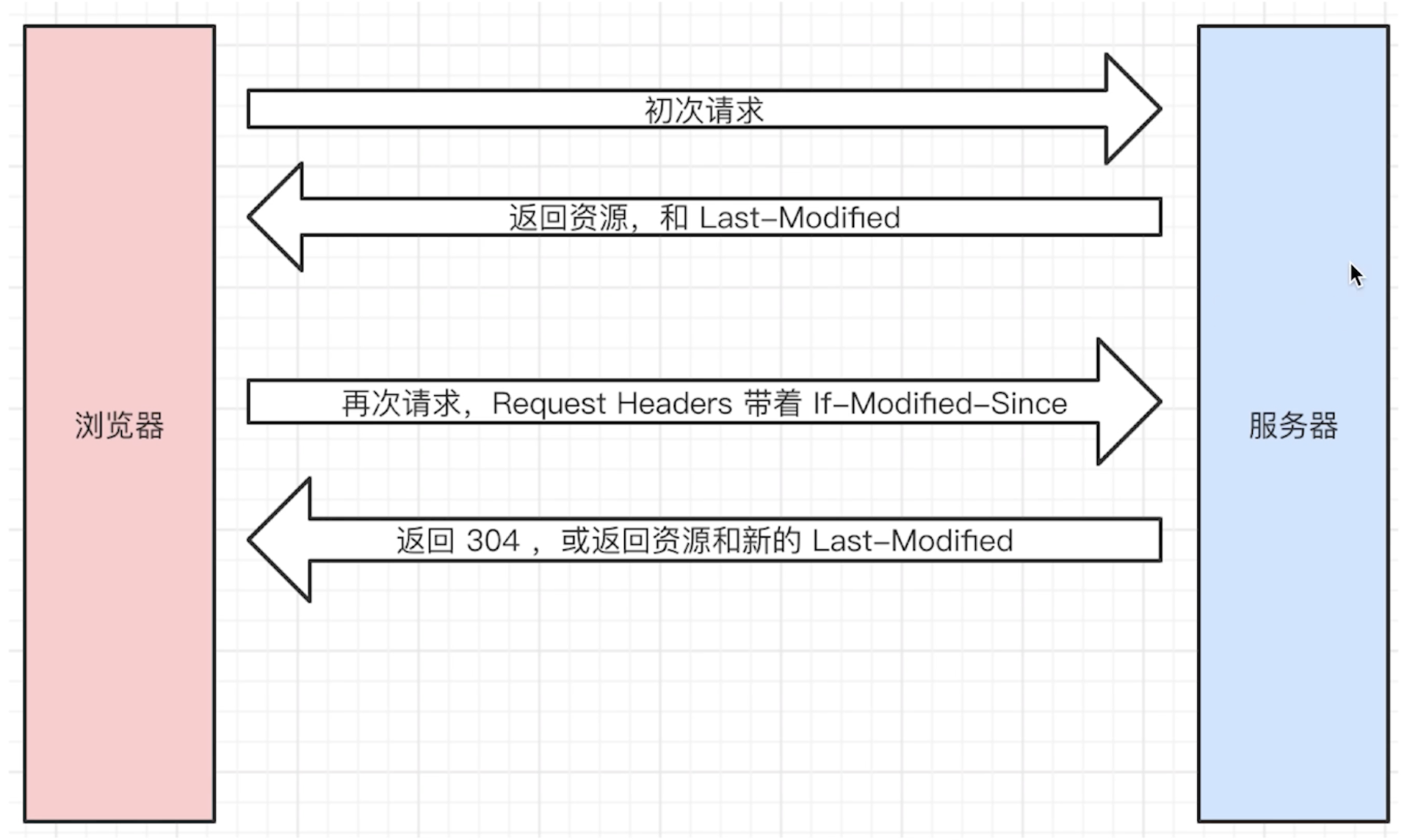
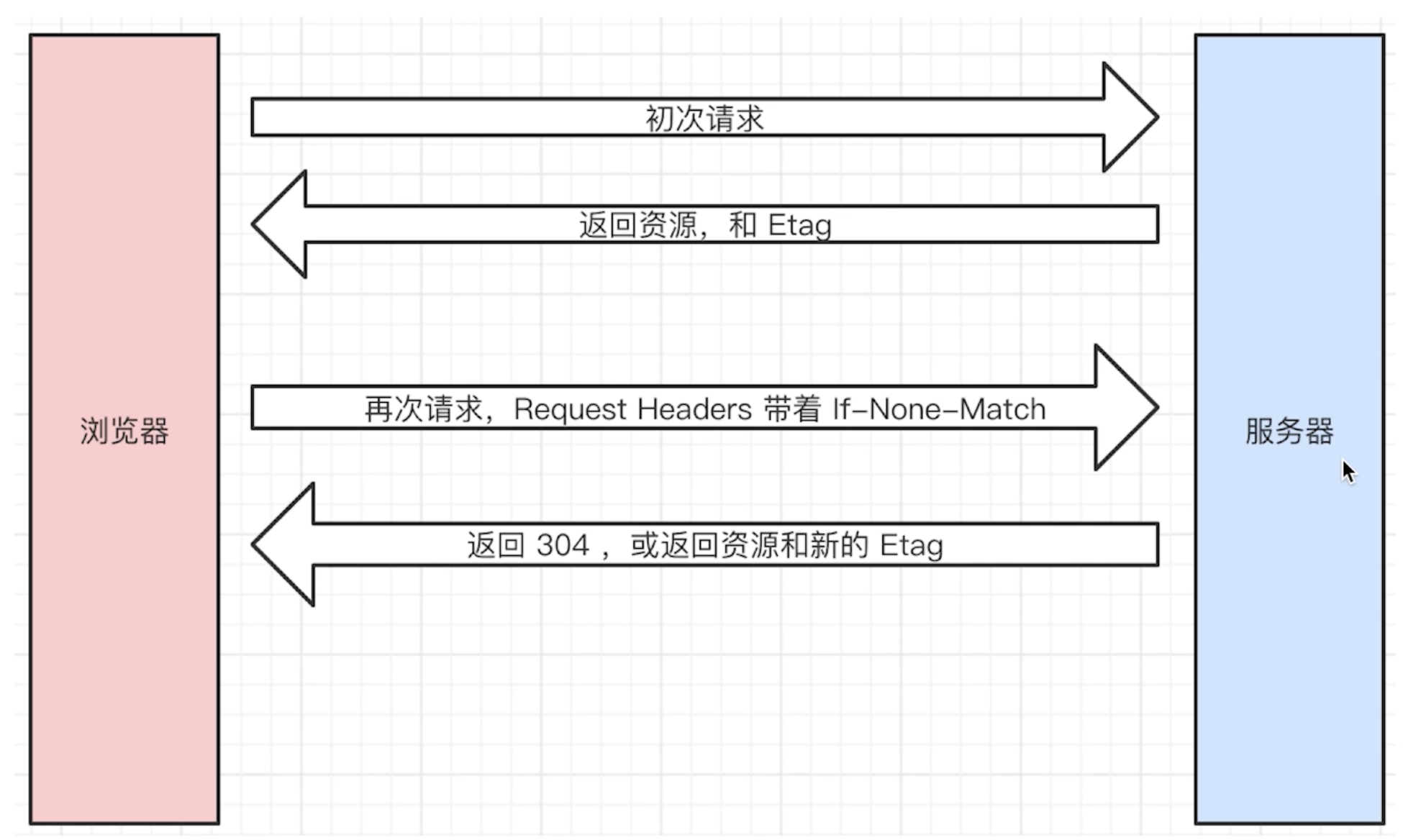
# 协商缓存(对比缓存)
- 服务器端缓存策略
- 服务器判断客户端资源,是否和服务端资源一样
- 一致则返回 304,否则返回 200 和最新的资源
 资源标识
资源标识
- 在 Response Headers 中,有两种
- Last-Modified 资源的最后修改时间
- Etag 资源的唯一标识(一个字符串,类似人类的指纹)
# Last-Modified 和 Etag
- 会优先使用 Etag
- Last-Modified 只能精确到秒级
- 如果资源被复生成,而内容不变,则 Etag 更精确
# 运行环境
# window.onload 和 DOMContentLoaded
window.addEventListener("load", function() {
// 页面的全部资源加载完才会执行,包括图片、视频等
});
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
// DOM 渲染完即可执行,此时图片、视频还可能没有加载完
});
# 性能优化
- 多使用内存、缓存或其他方法
- 减少 CPU 计算量,减少网络加载耗时
- 适用于所有编程的性能优化 - 空间换时间
# 让加载更快
- 减少资源体积:压缩代码
- 减少访问次数:合并代码,SSR 服务器端渲染,缓存
- 使用更快的网络:CDN
# 让渲染更快
- CSS 放在 head,JS 放在 body 最下面
- 尽早开始执行 JS,用 DOMContentLoaded 触发
- 懒加载(图片懒加载,上滑加载更多)
- 对 DOM 查询进行缓存
- 频繁 DOM 操作,合并到一起插入 DOM 结构
- 节流 throttle 防抖 debounce
# 防抖(debounce)
function debounce(fn, delay = 500) {
// timer在闭包中
let timer = null;
return function() {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, arguments);
timer = null;
}, delay);
};
}
# 节流(throttle)
function throttle(fn, delay) {
let timer = null;
return function() {
if (timer) return;
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, arguments);
timer = null;
}, delay);
};
}
# 安全
# XSS 跨站请求攻击
- 一个博客网站,我发表一篇博客,其中嵌入
<script>脚本 - 脚本内容:获取 cookie,发送到我的服务器(服务器配合跨域)
- 发布这篇博客,有人查看它,轻松收割访问者的 cookie
预防
- 替换特殊字符,如<变为
<,>变为> <script>变为<script>,直接显示,而不会作为脚本执行- 前端要替换,后端也要替换,都做总不会有错
# XSRF 跨站请求伪造
预防
- 使用 post 接口
- 增加验证,例如密码、短信验证码、指纹等
# 真题
# 数组 slice 和 splice 区别
- slice 为纯函数(不改变原数组,返回一个数组),splice 不是纯函数
- splice 可用于在数组中添加元素
# [10, 20, 30].map(parseInt)
拆解该题
[10, 20, 30].map((item, index) => {
return parseInt(item, index);
});
# 函数声明和函数表达式的区别
- 函数声明会在代码执行前预加载,而函数表达式不会
# new Object() 和 Object.create() 区别
- {}等同于 new Object(),原型 Object.prototype
- Object.create(null)没有原型
- Object.create({})可指定原型
# 实现new
function _new(fn, ...arg) {
const obj = Object.create(fn.prototype);
const result = fn.apply(obj, arg);
// 未返回对象则返回this
return result instanceof Object ? result : obj;
}
# 作用域和自由变量场景题
let i;
for (i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(i);
}, 1000);
}
1 秒钟后打印 4 个 4
let a = 100;
function test() {
alert(a);
a = 10;
alert(a);
}
test();
alert(a); // 此时a被 a=10 覆盖
// 输出100 10 10
# 手写字符串 trim 方法,保证兼容性
String.prototype.trim = function() {
return this.replace(/^\s+/, "").replace(/\s+$/, "");
};
# 手写 Math.max 方法
function max() {
const nums = [...arguments];
let max = 0;
nums.forEach((n) => {
if (n > max) {
max = n;
}
});
return max;
}
# 如何捕获 JS 中异常
- 方法一
try {
} catch (e) {
} finally {
}
- 方法二
window.onerror = function() {};
// 对跨域的 js,如 CDN 的,不会有详细的报错信息
// 对于压缩的 js,还要配合 sourceMap 反查到未压缩代码的行、列
# 什么是 JSON
- json 是一种数据格式,本质是一段字符串
- json 格式和 JS 对象结构一致,对 JS 语言更友好
- window.JSON 是一个全局对象:JSON.stringify、JSON.parse
# 获取当前页面 url 参数
- 传统方式,查找 location.search
function query(name) {
// 去掉?,仅保留a=1&b=2
const search = location.search.substring(1);
// 正则匹配
const reg = new RegExp(`(^|&)${name}=([^&]*)(&|$)`, "i");
const res = search.match(reg);
if (res === null) {
return null;
}
return res[2];
}
// query("b");
- 新 API,URLSearchParams
function query(name) {
const search = location.search;
const p = new URLSearchParams(search);
return p.get(name);
}
// query("b");
# 手写数组 flat
function flat(arr) {
// 验证arr中是否还有深层数组
const isDeep = arr.some((item) => Array.isArray(item));
if (!isDeep) {
return arr;
}
// 类似于[].concat([1,2,3,4])
const res = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arr);
return flat(res);
}
# 数组去重
function unique(arr) {
const set = new Set(arr);
return [...set];
}
console.log(unique([1, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 3]));
# 介绍 RFA(requestAnimationFrame)
- 要想动画流畅,更新频率要 60 帧/s,即 16.67ms 更新一次视图
- setTimeout 要手动控制频率,而 RAF 浏览器会自动控制
- 后台标签或隐藏 iframe 中,RAF 会暂停,而 setTimeout 依然执行
const div1 = document.getElementsByClassName("div1")[0];
let curWidth = 100;
const maxWidth = 640;
// 3s 把宽度从 100px 变为 640px,即增加 540px
// 60帧/s,3s 180 帧,每次变化 3px
function animate() {
curWidth = curWidth + 3;
div1.style.width = curWidth + "px";
if (curWidth < maxWidth) {
window.requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
}
animate();
