# React
# 事件
<div onClick={this.handleClick}>点击</div>;
handleClick = (event) => {
console.log("event", event);
console.log(event.nativeEvent.target); // 触发事件的div元素
console.log(event.nativeEvent.currentTarget); // react17后绑定到root组件上
};
# 表单
- 受控组件
- 非受控组件
# setState
- 不可变值(纯函数)
- 异步的(无法立刻获取最新值) react18 中 setTimeout、事件监听器中均是异步的
- 可能批量合并处理
// 传入对象会被合并,执行结果只+1
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
});
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
});
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1,
});
// 传入函数不会被合并,执行结果+3
this.setState((prevState) => {
// prevState为上次的值
return {
count: prevState.count + 1,
};
});
this.setState((prevState) => {
return {
count: prevState.count + 1,
};
});
this.setState((prevState) => {
return {
count: prevState.count + 1,
};
});
# 生命周期
# 单组件生命周期
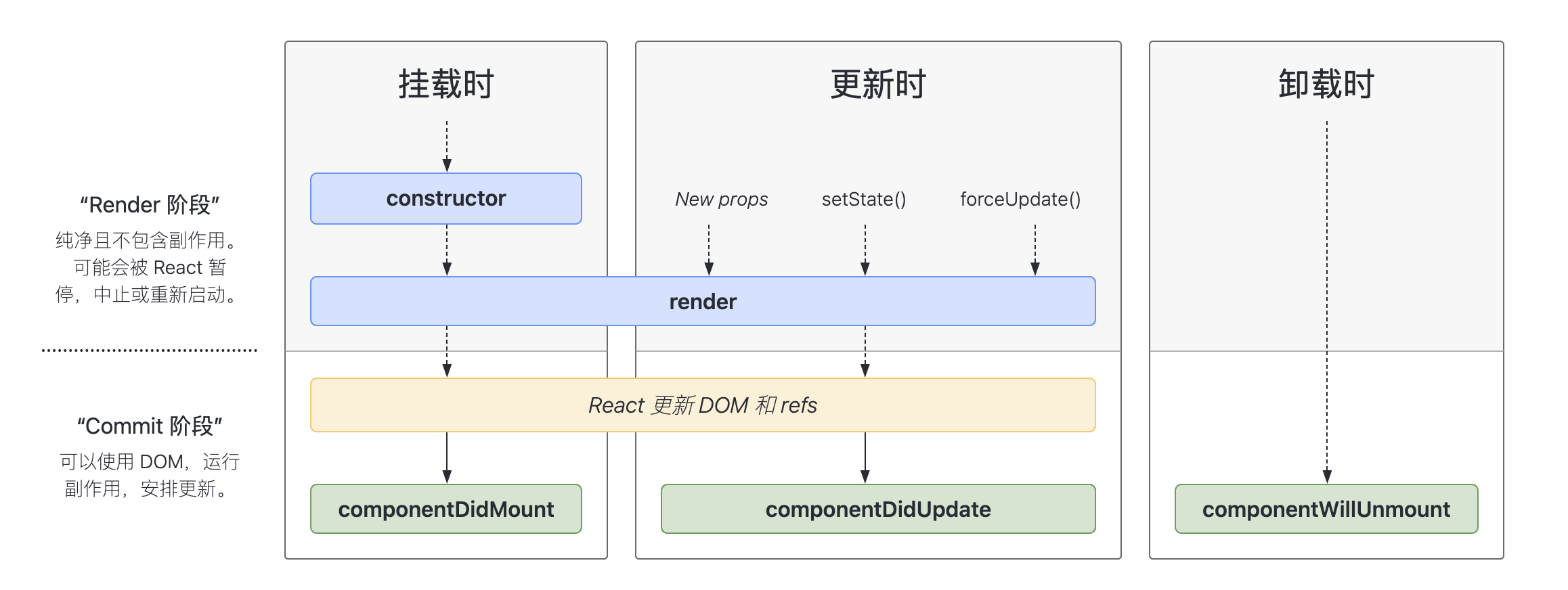
# 父子组件生命周期
和 Vue 相同
# 高级特性
- 函数组件
- 非受控组件
- Portals
- context
- 异步组件
- 性能优化
- 高阶组件 HOC
- Render Props
# 函数组件
- 纯函数,输入 props,输出 JSX
- 没有实例,没有生命周期,没有 state
- 不能扩展其他方法
# 非受控组件
- ref
- defaultValue defaultChecked
- 手动操作 DOM 元素
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: "zzj",
};
this.nameInputRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input defaultValue={this.state.name} ref={this.nameInputRef} />
<span>state.name:{this.state.name}</span>
<button onClick={this.alertName}>alert name</button>
</div>
);
}
alertName = () => {
// 通过ref获取DOM节点
const elem = this.nameInputRef.current;
alert(elem.value);
};
使用场景
- 必须手动操作 DOM 元素,setState 实现不了
- 文件上传
<input type="file" /> - 某些富文本编辑器,需要传入 DOM 元素
受控组件 vs 非受控组件
- 优先使用受控组件,符合 React 设计原则
- 必须操作 DOM 时,再使用非受控组件
# Portals
类似于 Vue3 中传送门 Teleport
使用场景
- overflow: hidden
- 父组件 z-index 值太小
- fixed 需要放在 body 第一层级
# context
const ThemeContext = React.createContext("light");
// class组件使用方式
class ThemeButton extends React.Component {
static contextType = ThemeContext;
render() {
const theme = this.context;
return <div>button theme is {theme}</div>;
}
}
// 函数组件使用方式
function ThemeLink() {
return (
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{(value) => <p>link theme is {value}</p>}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
);
}
function ToolBar() {
return (
<div>
<ThemeButton></ThemeButton>
<ThemeLink></ThemeLink>
</div>
);
}
class ContextDemo extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
theme: "light",
};
}
render() {
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={this.state.theme}>
<ToolBar></ToolBar>
<hr />
<button onClick={this.changeTheme}>change theme</button>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}
changeTheme = () => {
this.setState({
theme: this.state.theme === "light" ? "dark" : "light",
});
};
}
# 异步组件
- import
- React.lazy
- React.Suspense
import React, { lazy, Suspense } from "react";
const ContextDemo = lazy(() => import("./ContextDemo"));
render() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<ContextDemo></ContextDemo>
</Suspense>
);
}
# 高阶组件 HOC
const withMouse = (Component) => {
class withMouseComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
x: 0,
y: 0,
};
}
// 公共组件
handleMouseMove = (event) => {
this.setState({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div style={{ height: "500px" }} onMouseMove={this.handleMouseMove}>
{/* 1. 透传所有 props 2. 增加 mouse 属性 */}
<Component {...this.props} mouse={this.state}></Component>
</div>
);
}
}
return withMouseComponent;
};
redux connect 是高阶组件
# Render Props
import React from "react";
class Mouse extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { x: 0, y: 0 };
}
handleMouseMove = (event) => {
this.setState({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY,
});
};
render() {
return (
<div style={{ height: "500px" }} onMouseMove={this.handleMouseMove}>
{this.props.render(this.state)}
</div>
);
}
}
const App = () => {
return (
<Mouse
render={({ x, y }) => (
<h1>
the mouse position is {x}-{y}
</h1>
)}
></Mouse>
);
};
export default App;
# 性能优化
- shouldComponentUpdate(简称 SCU)
- PureComponent 和 React.memo
- 不可变值 immutable.js
# shouldComponentUpdate
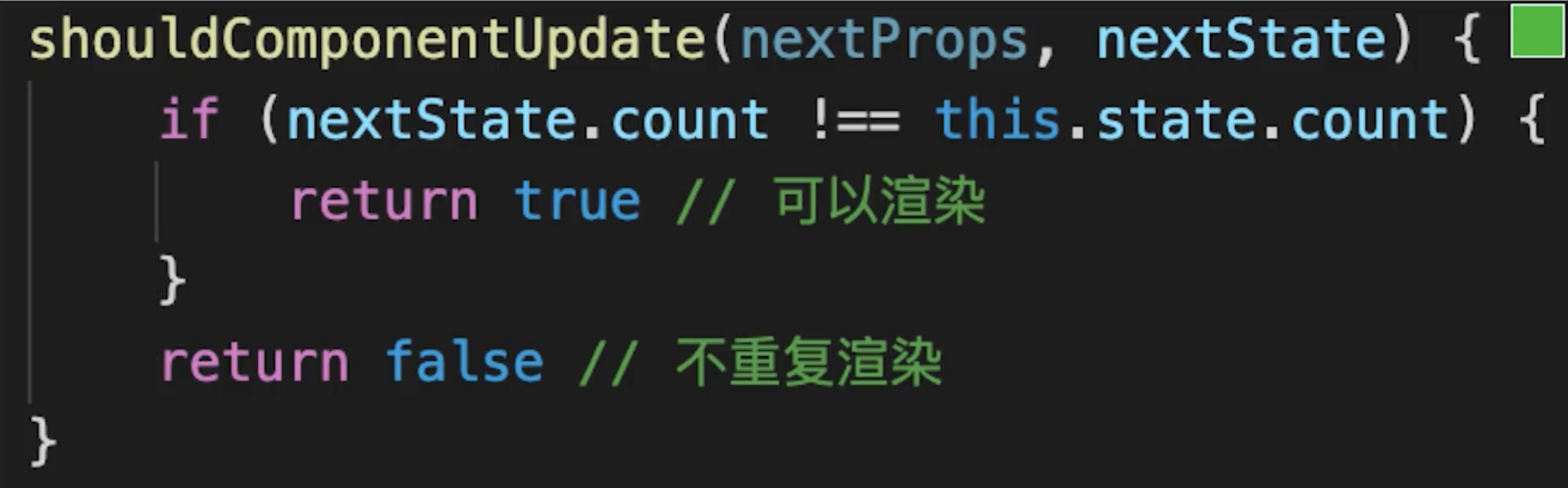
React 默认:父组件有更新,子组件也无条件更新
# SCU 使用总结
- SCU 默认返回 true,即 React 默认重新渲染所有子组件
- 必须配合“不可变值”一起使用
- 可先不用 SCU,有性能问题时再考虑使用
# PureComponent
PureComponent, SCU 中实现了浅比较
# memo
memo,函数组件中的 PureComponent
# immutable.js
- 彻底拥抱“不可变值”
- 基于共享数据(不是深拷贝),速度快
- 有一定学习和迁移成本,按需使用
# Redux
- store state
- action
- reducer
# 单向数据流概述
- dispatch(action)
- reducer -> newState
- subscribe 触发通知
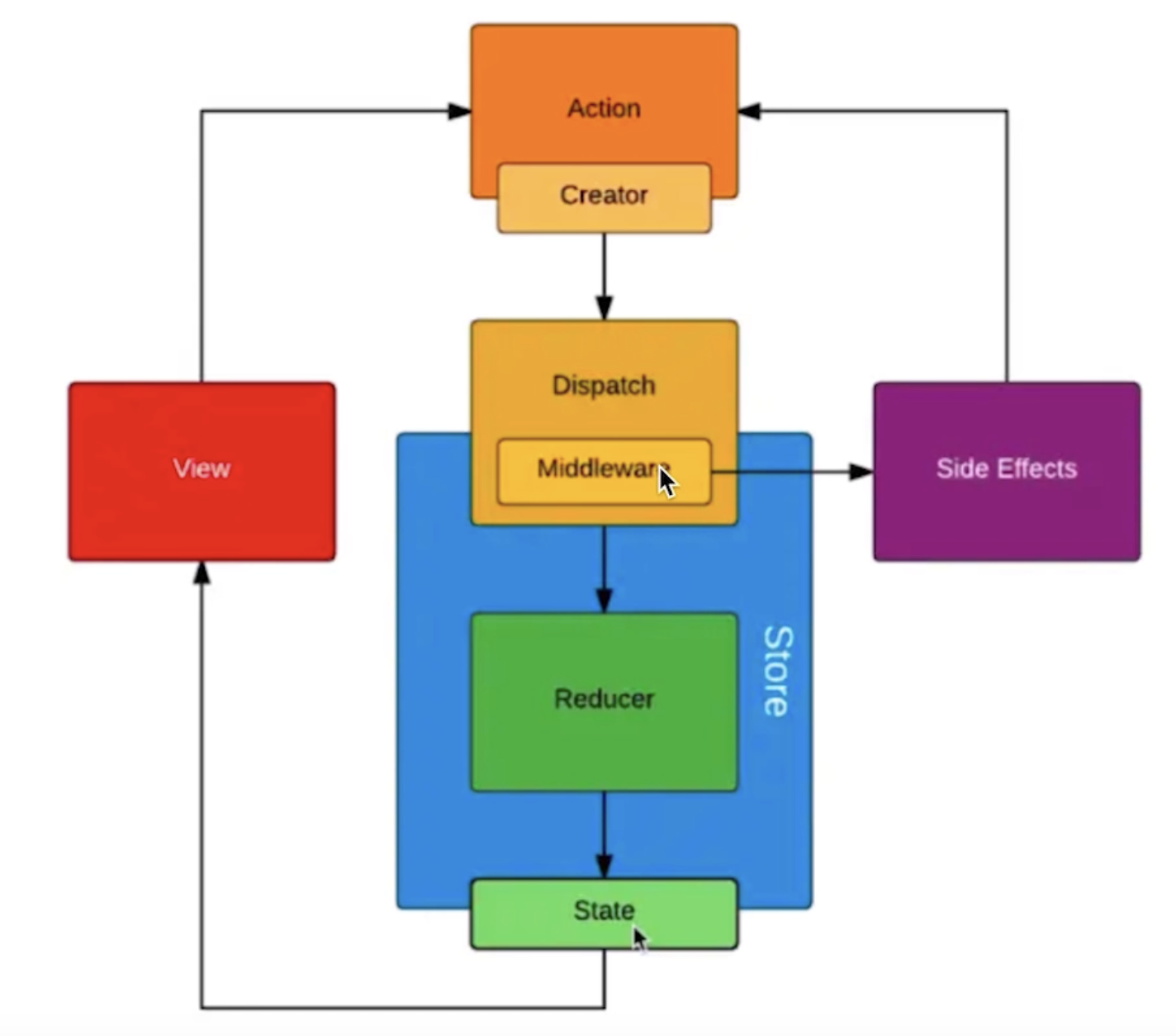
# React Redux
- Provider
- connect
- mapStateToProps 和 mapDispatchToProps
# action
- 同步 action
export const addTodo = (text) => ({
type: "ADD_TODO",
id: nextTodoId++,
text,
});
- 异步 action(返回一个函数)
export const addTodoAsync = (text) => {
return (dispatch) => {
fetch(url).then((res) => {
// 执行异步action
dispatch(addTodo(res.text));
});
};
};
- redux-thunk
- redux-promise
- redux-saga
# Redux 中间件

# React 原理
- 函数式编程
- vdom 和 diff
- JSX 本质
- 合成事件
- setState batchUpdate
- 组件渲染过程
# 函数式编程
- 纯函数
- 不可变值
# vdom 和 diff
- h 函数
- vnode 数据结构
- patch 函数
- 只比较同一层级,不跨级比较
- tag 不相同,则直接删掉重建 ,不再深度比较
- tag 和 key ,两者都相同,则认为是相同节点,不再深度比较
# JSX 本质
- 本质即 createElement 函数
- 执行返回 vnode
# 合成事件
- 所有事件挂载到 root 上
- event 不是原生的,是 SyntheticEvent 合成事件对象
- 和 Vue 事件不同,和 DOM 事件也不同
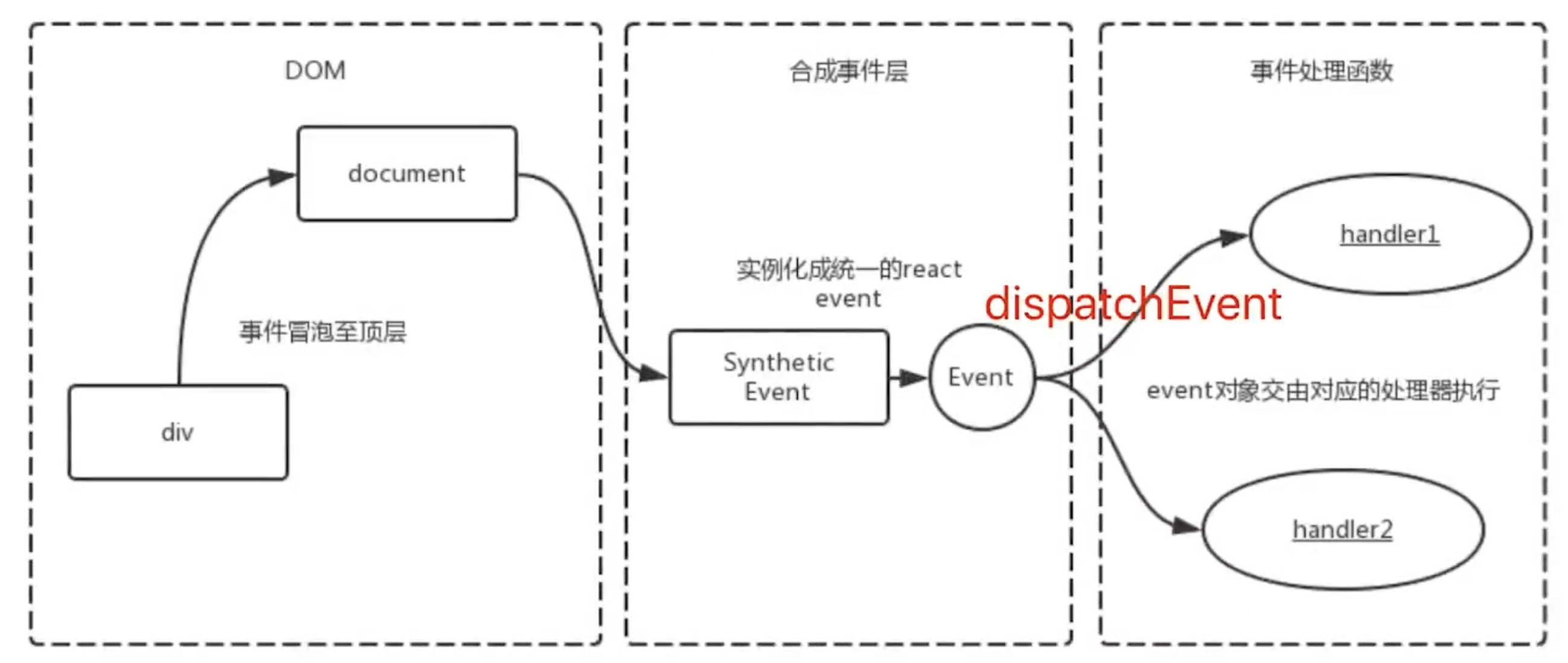
为何要合成事件机制
- 更好的兼容性和跨平台
- 挂载到 document,减少内存消耗,避免频繁解绑
- 方便事件的统一管理(如事务机制)
# setState 和 batchUpdate
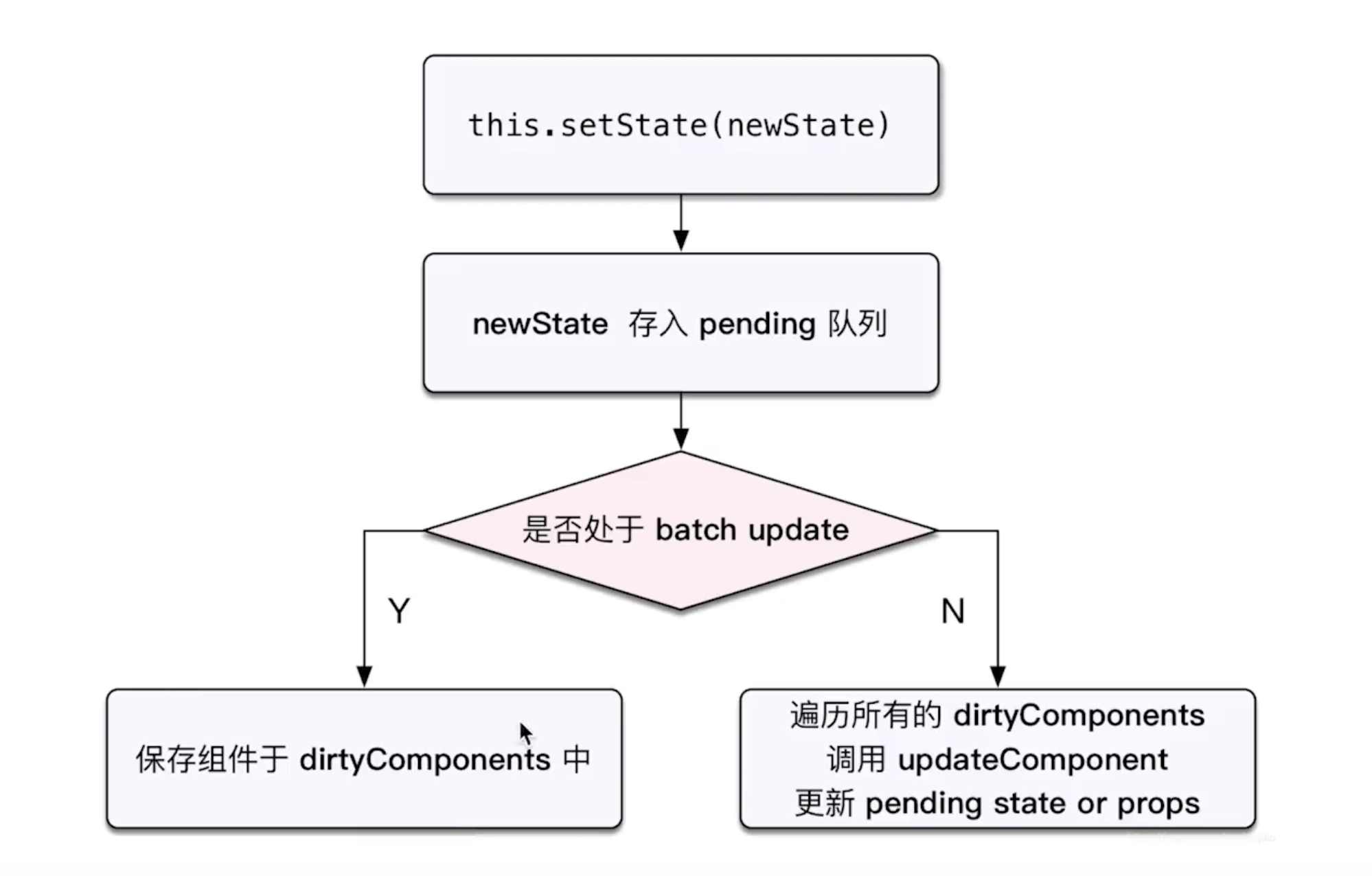
哪些能命中 batchUpdate 机制
- 生命周期(和它调用的函数)
- React 中注册的事件(和它调用的函数)
- React 可以“管理”的入口
# React fiber
- 将 reconciliation 阶段进行任务拆分(commit 无法拆分)
- DOM 需要渲染时暂停,空闲时恢复
- window.requestIdleCallback
# React Hooks
# 函数组件的特点
- 没有组件实例
- 没有生命周期
- 没有 state 和 setState,只能接收 props
# setState
useState(0)传入初始值,返回数组[state, setState]- 通过
state获取值、 - 通过
setState(1)修改值
# useEffect 模拟组件生命周期
- 模拟 DidMount 和 DidUpdate
// DidMount 和 DidUpdate下面均会打印
useEffect(() => {
console.log("在此发送一个 ajax 请求");
});
- 模拟 DidMount
useEffect(() => {
console.log("加载完了");
}, []); // 第二个参数是 [] (不依赖于任何 state)
- 模拟 DidUpdate
useEffect(() => {
console.log("更新了");
}, [count]); // 第二个参数就是依赖的 state
- 模拟 WillUnMount
useEffect(() => {
let timerId = window.setInterval(() => {
console.log(Date.now());
}, 1000);
// 返回一个函数,模拟 WillUnMount
return () => {
window.clearInterval(timerId);
};
}, []);
- 不完全等同于 WillUnMount
// DidMount 和 DidUpdate
useEffect(() => {
console.log(`开始监听 ${friendId} 在线状态`);
// 此处并不完全等同于 WillUnMount
// props 发生变化,即更新,也会执行结束监听
// 返回的函数,会在下一次 effect 执行之前,被执行
return () => {
console.log(`结束监听 ${friendId} 在线状态`);
};
});
# useRef
获取 DOM 节点
function UseRef() {
const btnRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
// DOM 节点
console.log(btnRef.current);
}, []);
return (
<div>
<button ref={btnRef}>click</button>
</div>
);
}
# useContext
import React, { useContext } from "react";
// 主题颜色
const themes = {
light: {
foreground: "#000",
background: "#eee",
},
dark: {
foreground: "#fff",
background: "#222",
},
};
// 创建 Context
const ThemeContext = React.createContext(themes.light);
function ThemeButton() {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<button style={{ background: theme.background, color: theme.foreground }}>
hello world
</button>
);
}
function Toolbar() {
return <ThemeButton></ThemeButton>;
}
function App() {
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={themes.dark}>
<Toolbar></Toolbar>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
}
# useReducer
import React, { useReducer } from "react";
const initialState = { count: 0 };
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case "increment":
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case "decrement":
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
return state;
}
};
function App() {
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
return (
<div>
count: {state.count}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: "increment" })}>increment</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: "decrement" })}>decrement</button>
</div>
);
}
- useReducer 是 useState 的代替方案,用于 state 复杂变化
- useReducer 是单个组件状态管理,组件通讯还需要 props
- redux 是全局的状态管理,多组件共享数据
# useMemo
// 类似 class PureComponent,对 props 进行浅层比较
const Child = memo(({ userInfo }) => {
console.log("Child render...", userInfo);
return (
<div>
<p>
This is Child {userInfo.name} {userInfo.age}
</p>
</div>
);
});
// 父组件
function App() {
console.log("Parent render...");
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [name, setName] = useState("测试用户");
// 用 useMemo 缓存数据,name 变化时子组件才会更新
const userInfo = useMemo(() => {
return { name, age: 21 };
}, [name]);
return (
<div>
<p>
count is {count}
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>click</button>
</p>
<Child userInfo={userInfo}></Child>
</div>
);
}
- React 默认会更新所有子组件
- class 组件使用 SCU 和 PureComponent 做优化
- Hooks 中使用 useMemo,但优化的原理是相同的
# useCallback
向子组件传入函数,useMemo 失效,所以需要使用 useCallback
const Child = memo(({ userInfo, onChange }) => {
console.log("Child render...", userInfo);
return (
<div>
<p>
This is Child {userInfo.name} {userInfo.age}
</p>
<input onChange={onChange}></input>
</div>
);
});
// 父组件
function App() {
console.log("Parent render...");
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [name, setName] = useState("测试用户");
// 用 useMemo 缓存数据
const userInfo = useMemo(() => {
return { name, age: 21 };
}, [name]);
// 用 useCallback 缓存函数
const onChange = useCallback((e) => {
console.log(e.target.value);
}, []);
return (
<div>
<p>
count is {count}
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>click</button>
</p>
<Child userInfo={userInfo} onChange={onChange}></Child>
</div>
);
}
# 自定义 hooks
// 封装 axios 发送网络请求的自定义 Hook
function useAxios(url) {
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
const [data, setData] = useState();
const [error, setError] = useState();
useEffect(() => {
// 利用 axios 发送网络请求
setLoading(true);
axios
.get(url) // 发送一个 get 请求
.then((res) => setData(res))
.catch((err) => setError(err))
.finally(() => setLoading(false));
}, [url]);
return [loading, data, error];
}
export default useAxios;
# Hooks 使用规范
- 只能用于 React 函数组件和自定义 Hook 中,其他地方不可以
- 只能用于顶层代码,不能在循环、判断中使用 Hooks
- eslint 插件 eslint-plugin-react-hooks 可以帮到你
# React Hooks 注意事项
- useState 初始化值,只有第一次有效
// 子组件
function Child({ userInfo }) {
// render: 初始化 state
// re-render: userInfo.name变化后,name不会重新设置新的值,只能用 setName 修改
const [name, setName] = useState(userInfo.name);
return (
<div>
<p>Child, props name: {userInfo.name}</p>
<p>Child, state name: {name}</p>
</div>
);
}
- useEffect 内部不能修改 state
function UseEffectChangeState() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
console.log("useEffect...", count);
const timer = setInterval(() => {
console.log("setInterval...", count); // 一直为0
setCount(count + 1);
}, 1000);
return () => clearTimeout(timer);
}, []);
// 依赖为 [] 时: re-render 不会重新执行 effect 函数
// 删除 [] 后:re-render 会重新执行 effect 函数
return <div>count: {count}</div>;
}
- useEffect 可能出现死循环
// useEffect 依赖值最好不为对象或者数组,引用类型地址一直变化
useEffect(() => {
const timer = setInterval(() => {
console.log("setInterval...", count); // 一直为0
setCount(count + 1);
}, 1000);
return () => clearTimeout(timer);
}, {});
# 面试真题
# 组件间通信
- 父子组件 props
- 自定义事件(new CustomEvent)
class EventBus {
constructor() {
this.bus = document.createElement("fakeElement");
}
addEventListener(event, callback) {
this.bus.addEventListener(event, callback);
}
removeEventListener(event, callback) {
this.bus.removeEventListener(event, callback);
}
dispatchEvent(event, detail = {}) {
this.bus.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent(event, { detail }));
}
}
export default new EventBus();
- Redux 和 Context
# React 发送 ajax 应该在哪个生命周期
- componentDidMount
# 渲染列表为何使用 key
- 必须用 key,且不能是 index 和 random
- diff 算法中通过 tag 和 key 来判断,是否是 sameNode
- 减少渲染次数,提升渲染性能
# 函数组件和 class 组件区别
- 纯函数,输入 props,输出 JSX
- 没有实例,没有生命周期,没有 state
- 不能扩展其他方法
# 受控组件
- 表单的值,受 state 控制
- 需要自行监听 onChange,更新 state
# 多个组件有公共逻辑,如何抽离
- 高阶组件
- Render Props
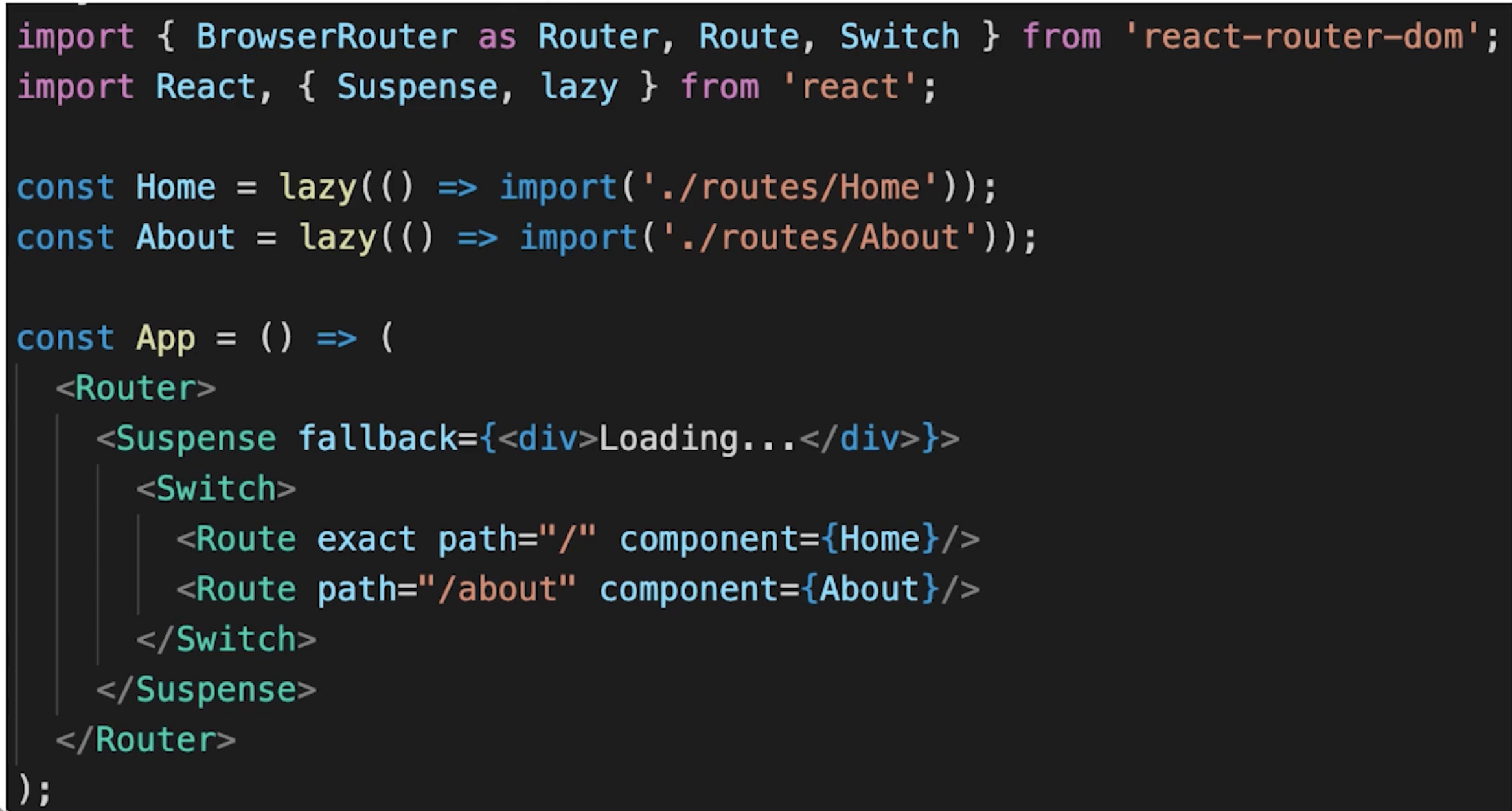
# react-router 如何配置懒加载
# React 性能优化
- 渲染列表时加 key
- 自定义事件、DOM 事件及时销毁
- 合理使用异步组件
- 减少函数 bind this 的次数
- 合理使用 SCU PureComponent 和 memo
- 合理使用 immutable.js
# React 和 Vue 区别
- 都支持组件化
- 都是数据驱动视图
- 都使用 vdom 操作 DOM
- React 使用 JSX 拥抱 JS,Vue 使用模板拥抱 html
- React 函数式编程,Vue 声明式编程
# class 组件的问题
- 大型组件很难拆分和重构,很难测试(即 class 不易拆分)
- 相同业务逻辑,分散到各个方法中,逻辑混乱
- 复用逻辑变的复杂,如 Mixins、HOC、Render Prop
# 为什么要使用 Hooks
- 完善函数组件的能力,函数更适合 React 组件
- 组件逻辑复用,Hooks 表现更好
- class 复杂组件正在变得费解,不易拆解,不易测试,逻辑混乱
# React Hooks 性能优化
- useMemo 缓存数据
- useCallback 缓存函数
- 相当于 class 组件的 SCU 和 PureComponent
